I get to speak at this faculty studded event.
12/4/21
11/29/21
11/21/21
The Big Game
Kinda thrilled to see 2 Big Game wins (Stanford/Cal friendly rivalry) during my time here at Cal.
And it was a resounding win too with 2 records.
10/28/21
Why Inspiration Porn is Harmful
PlainSpeak. In Plain Language for Lay Reader
Inspiration porn is a term used to describe when disabled people are shown as being super inspirational just for doing everyday things because they have a disability. This kind of portrayal often makes it seem like being disabled automatically makes someone a hero, which isn't fair or accurate.
A common example of inspiration porn might be a story about a disabled person graduating from school, which gets a lot of attention because people see it as overcoming something amazing. But the truth is, disabled people face many challenges, and they don't want to be celebrated just for doing what others do—they want to be seen as people first.
This kind of portrayal can be harmful because it often ignores the real issues disabled people face, like lack of access to education, jobs, or even basic facilities. It also makes it seem like if one disabled person can succeed, then others should be able to do the same without help, which isn't true or fair.
Inspiration porn can make people without disabilities feel good about themselves, but it doesn't help disabled people. It actually hurts them because it reduces their experiences to feel-good stories, instead of recognizing the real barriers they face and the real solutions they need.
To really help, we need to stop looking at disabled people as just sources of inspiration and start seeing them as individuals who deserve equal opportunities and respect. This means working on real changes in society, like better accessibility and fighting against discrimination, so everyone can live their lives fully and fairly.
10/15/21
Lucid Dreaming
Lucid Dreaming is a state during REM sleep where individuals become aware they are dreaming and can often exert control over the dream environment. Research suggests a possible connection between autism and lucid dreaming, with autistics potentially experiencing lucid dreams more frequently, possibly due to differences in sensory and cognitive processing. [Read in more detail]
PlainSpeak. Lucid Dreaming is when you're dreaming and realize it, sometimes even changing what happens in the dream. Autistic individuals might have lucid dreams more often, possibly because they notice details more easily, but more research is needed to understand why this happens. [Read in more detail]
10/13/21
Campus Change Maker
This is so cool. Thank you UC Berkeley.
Bringing Disability Awareness & Visibility to Sproul Plaza!
Visit our table on Sproul Plaza today from 9 to noon to connect with student groups and campus resources including: The Disabled Students Commission, Berkeley Disabled Students Group (BDS), Spectrum at Cal, OCD at Cal, CAPS, RSF, DSP, and the DCC!
As part of Disability Awareness Month celebrations, we are uplifting the work and stories of a series of Change Makers from the Disability Community. This week, we are highlighting the contributions of Hari Srinivasan. Undergraduate student, instructor of the Autism DeCal, and journalist at the Daily Cal.
Image Description: A photo of Hari standing on a bridge on UC Berkeley's campus. Text reads: Hari Srinivasan. Undergraduate student and instructor. There is a quote from Hari next to it that reads, "I want you to think of disability as possibility too. Only when you think of possibility can the door of opportunity be opened."
Recruiting autistic participants for Research Study
Please participate if you are above age 18, autistic and live in the US.
10/12/21
10/10/21
Insights from CBT
This is not my fault
I didn't do this on purpose.
It's not fair to judge myself, because its not accurate to judge yourself.
Remind myself, Don't judge myself for judging myself.
10/8/21
10/4/21
What is Neuronal Pruning
What is Neuronal Pruning?
Neuronal pruning is like a natural "trimming" process in the brain that happens as we grow. During this process, the brain gets rid of extra neurons and connections it doesn't need, helping it to work more efficiently. Think of it like pruning a tree to help it grow better.
How is it Related to Autism?
In autism, including a form called regressive autism, there may be differences in this pruning process. Some researchers think that if pruning is either too much or too little, it can cause problems. For example:
- Excessive Pruning: If the brain removes too many connections, important ones needed for learning and communication might be lost.
- Insufficient Pruning: If not enough pruning happens, the brain might end up with too many connections, which can cause confusion and make it hard to process information.
Evidence from Studies:
Studies using brain imaging techniques like MRI have shown that autistics might have more connections in some parts of their brains. This suggests that their brains may not prune as much as they should. Postmortem studies (studies done after a person has passed away) have found similar patterns, supporting the idea that altered pruning could be involved in autism.
Genetic Factors:
Some genes that help control the pruning process have been found to work differently in people with autism. For example, changes in genes like MECP2, SHANK3, and PTEN might lead to problems with pruning and have been linked to autism.
Why is This Important in Regressive Autism?
In regressive autism, where children lose skills they had previously developed, disrupted pruning might play a role. This abnormal pruning could affect the brain areas involved in language, social interaction, and behavior, leading to the sudden changes seen in these children. This explanation helps to understand how natural brain processes like pruning might be different in people with autism, potentially affecting how they learn and interact with the world.
Citations
- Tang, G., et al. (2014). Loss of mTOR-dependent macroautophagy causes autistic-like synaptic pruning deficits. Neuron, 83(5), 1131-1143.
- Varghese, M., et al. (2017). Autism spectrum disorder: neuropathology and animal models. Acta Neuropathologica, 134(4), 537-566.
- Penzes, P., et al. (2011). Dendritic spine pathology in neuropsychiatric disorders. Nature Neuroscience, 14(3), 285-293.
10/1/21
9/30/21
Flat Affect in Autism: What It Means
Flat affect, sometimes called "flat effect," is when a person shows less emotion on their face, in their voice, and with their body movements. This is common in some autistic people. Here’s what it looks like:
- They might not smile or frown much.
- Their voice might sound the same most of the time, without much change in tone.
- They might not use many hand movements or gestures when talking.
Just because someone has a flat affect doesn’t mean they don’t feel emotions. They still have feelings, but it’s harder for others to see them.
This can make social interactions tricky. People might think someone with a flat affect is not interested or doesn’t care, even if that’s not true. Understanding flat affect helps us communicate better and connect with autistic people who show emotions differently.
===========================================================
Versions of this post: Academic/Scientific Audience & PlainSpeak for LayReader
Other articles in #PlainSpeak
Take Care and Don't Ever Give up
Hi Hari,
I hope this email finds you well
I am writing from Perth, Australia. I am writing just to let you know that I have found your message and story inspiring
I am the father of a 6 year old autistic boy and I cannot stress enough how your work and messages has giving me so many ideas to assist my little one to live in a non-autistic ready world
Take care and don't ever give up
9/29/21
Believe in the Impossible.
9/27/21
9/24/21
Aspie - Aspergers
Before the release of the DSM-5 in 2013, autism and Asperger's Syndrome (or Aspie) were considered distinct diagnostic categories within the broader category of pervasive developmental disorders (PDD).
Diagnostic Criteria
Autism (Autistic Disorder):
- Social Interaction: Marked impairments in social interaction, including difficulties with nonverbal behaviors, developing peer relationships, and understanding social cues.
- Communication: Significant delays or abnormalities in language development, including a lack of spoken language or difficulty sustaining a conversation.
- Behavior: Presence of restricted, repetitive, and stereotyped patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
- Onset: Symptoms typically apparent before the age of three.
Asperger's Syndrome:
- Social Interaction: Similar to autism, Aspies exhibit significant difficulties in social interactions and understanding social norms.
- Communication: Unlike autism, there are no significant delays in language acquisition. Aspie's often have fluent speech and good verbal skills but may struggle with the pragmatic use of language (e.g., understanding humor or sarcasm).
- Behavior: Similar to autism, there are restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests.
- Cognitive Development: No significant delay in cognitive development or self-help skills. In fact, individuals often have average to above-average intelligence.
- Onset: Symptoms might not be as apparent at an early age, often becoming noticeable when social demands increase.
Functional Impact
- Autism: Often associated with more significant challenges across multiple areas of functioning due to the presence of language delays and more pronounced social and behavioral difficulties.
- Asperger's Syndrome: Typically associated with less severe challenges in early childhood due to intact language and cognitive development. However, social difficulties become more apparent in later childhood and adolescence.
Evolution in DSM-5
With the introduction of DSM-5, the separate diagnoses of autism, Asperger's Syndrome, and other related disorders (like Pervasive Developmental Disorder-Not Otherwise Specified, or PDD-NOS) were unified under the single diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This change was made to reflect the spectrum nature of the condition, acknowledging that these conditions share core features but vary in severity and expression.
Rationale for Change
- Continuum of Symptoms: The change recognizes that autism-related conditions exist on a spectrum, with varying degrees of severity and functional impact.
- Clinical Utility: Simplifies diagnosis by reducing the complexity and potential inconsistencies associated with distinguishing between related conditions.
- Research and Treatment: Facilitates more unified research efforts and the development of interventions that can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs, regardless of the previous diagnostic category.
Before 2013, autism and Asperger’s Syndrome (sometimes called "Aspie") were considered separate diagnoses within a group of conditions called pervasive developmental disorders (PDD).
Diagnostic Criteria
Autism (Autistic Disorder):
- Social Interaction: Big challenges with social skills, like reading body language, making friends, and understanding social cues.
- Communication: Delays in talking and language use, sometimes not talking at all or having trouble keeping a conversation going.
- Behavior: Repetitive movements and routines, and strong interests in specific things.
- Onset: Signs usually show up before the age of three.
Asperger’s Syndrome (Aspie):
- Social Interaction: Also have difficulties with social skills and understanding social norms, similar to autism.
- Communication: No major delays in learning to talk. Aspies usually have good language skills but may struggle with using language in social situations, like understanding jokes or sarcasm.
- Behavior: Similar repetitive movements and strong interests as in autism.
- Cognitive Development: No delays in learning or taking care of themselves. Often have average or above-average intelligence.
- Onset: Signs may not be noticeable until social situations become more demanding, often in later childhood or adolescence.
Functional Impact
Autism: Often has more severe challenges due to language delays and more noticeable social and behavioral difficulties.
Asperger’s Syndrome: Usually has fewer challenges in early childhood because of good language and learning skills, but social difficulties can become more apparent later on.
Changes with DSM-5
In 2013, the DSM-5 combined autism, Asperger’s Syndrome, and other related conditions (like PDD-NOS) into one diagnosis called Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This change was made to show that these conditions are part of a spectrum, meaning they share similar features but vary in how severe they are.
Why the Change?
- Continuum of Symptoms: Autism-related challenges are seen as part of a spectrum with different levels of severity and impact.
- Simplifying Diagnosis: Combining the conditions makes diagnosing easier and reduces confusion.
- Better Research and Treatment: It helps scientists and doctors create better treatments and support that fit each person’s specific needs.
9/23/21
Master of Ceremonies at ASAN Gala 2021

Join us for a special virtual edition of our annual celebration and fundraising event from Wednesday, November 17th through Friday, November 19th. We’re so excited to share the gala with disability community members and allies from across the country and around the world, who usually wouldn’t be able to attend in-person.
We’re happy to announce that Hari Srinivasan will be our Master of Ceremonies!
Image description: A young Indian American man in his 20s with black hair under a white baseball cap. He is wearing jeans and a long sleeved gray shirt that says California Golden Bears. He is standing next to a stone railing.
Hari Srinivasan is a minimally-speaking autistic student at UC Berkeley. He is on ASAN’s Board of Directors and a 2019 alumnus of our Autism Campus Inclusion program! At UC Berkeley, Hari is a student journalist for the Daily Californian, student instructor for a class on autism, research assistant at the UC Berkeley Psychology and Disability Labs, and was the first nonspeaking president of the student group, Autism:Spectrum At Cal. As a Haas Scholar, he is doing research on how autistic people experience awe. Hari was recently selected to serve on the Interagency Autism Coordinating Committee, which advises federal policy and priorities around autism. We are so grateful for Hari’s dedicated advocacy!
Hari hopes to bring attention to issues which impact disabled people in myriad areas and across the lifespan. He also wants to emphasize the urgency to include and address the issues faced by the more marginalized groups and higher support needs within the autism and larger disability community, including their mental, physical healthcare needs and comorbidities. When the voices of select groups get left out of the conversation, it negatively impacts their access to spaces, resources, funding, policy and quality of life.
We are full of autistic awe that Hari will host our annual gala and hope that you can come celebrate with us!
Gala tickets are donate-what-you-can, but no donation will be required to attend our virtual gala events. Proceeds will support our advocacy work and programs for the coming year, and allow us to continue working to empower disabled people across the country. If you’re able, please consider donating to support our work. If you are not able to donate, no worries -- we’re just happy to have you celebrating with us!
Honorees and other programming will be announced in the coming weeks.
You can RSVP to our Facebook event and invite your friends! We’re excited to celebrate together.
9/21/21
SPSS
Another first coming up. I will be presenting my research poster at SPSS conference next Feb.
My first Psychology conference.
Writing an abstract
My attempt at the abstract for my research project.
Past research on emotions has viewed autistics from a deficit perspective, as lacking in empathy, emotion recognition and emotional experience; even as other research posits autistic emotion experiences as more intense; and we hypothesize that this could also be true of the autistic experience of positive emotions such as awe. This first of its kind study, draws on the science of awe to examine how autistics perceive and view awe, an emotion shown to have transformative effects. This research looks at how these dimensions of emotion may diverge in autistics from what has been written from a neurotypical (non-autistic) lens. With a target sample size of n=200, the study makes use of existing self-report psychological measures of emotions, includes a new empathy measure in development by the Berkeley Social Interaction Lab, as well as written narratives, from both autistics and non-autistic controls. Data from this study will add to knowledge on: 1) autism & empathy/ emotion recognition, 2) autism & emotional experience, 3) autism & awe. Potential applications include additional tools such as “small doses of awe” that can be added to the coping and navigating toolbox for autistics.
9/19/21
All that's wrong with this letter from RC
All Indians MUST necessarily know Hindi,
ALL THAT’s WRONG WITH THIS LETTER on the Self-Determination Program from the CA Department of Developmental Services.
Someone at DDS decided that because I have an Indian origin last name.
1. My mother tongue must be HINDI; its not.
2. I MUST KNOW how to read the HINDI devanagari script.
3. An automatic presumption on the part on the Hindi-speaking person at DDS who came up with this plan, that every person of Indian origin knows Hindi.
Hindi is predominant in specific parts of the India only. Even if half the country knows Hindi, it marginalizes the remaining 650 million Indians in India who don't use it; the southern states being an example. There are 22 official languages in India…
I found this very insensitive; almost reflective of the autistic/disabled experience where neurotypicals/nondisabled will assume that theirs’ is the only experience that counts.
Why are they making information on disability services more inaccessible here in the CA and wasting taxpayer money in the process. How many trees died in printing out thousands of these letters, how many mailman hours were wasted in the delivery these letters.
Who got to decide this in CA; given its claim of being a more disability friendly state. This is really the last thing I expected in California.
9/17/21
9/14/21
9/12/21
The historical moment or event I i wish I had witnessed.
The event I would have like to have witnessed is Buddha, sitting under the Bodhi tree and opening his eyes after receiving enlightenment. The moment would truly have been transcendent, as he spoke to those assembled before him, giving a glimpse into the incredible insights he had gained.
9/11/21
9/10/21
Haas Scholars Fall Colloquium
Prof Dacher Keltner, Psychology: I think many of you know that Hari writes for the Daily Cal. When he was in my class, he would send me his poetry all the time. He is a brilliant writer and a brilliant thinker and I think you all felt that in that presentation. That was an incredible tour of 13 minutes and 47 seconds, from the personal to the humorous to the in-depth critique to the societal critique to the measures to the theory. I mean that, I’ve never felt, I’ve never had a presentation in my lab of that precision. The second thing is Hari’s presentation tells us why we need diversity in scholarship. His scholarship is just you know, its a devastating critique on measures and theories out there and we need these perspectives. What a rich perspective, so it was a remarkable presentation and he’s a remarkable young scholar.
9/9/21
#1 Public University
"UC Berkeley is the No. 1 U.S. public university, the sixth-best among publics and privates nationally and the world’s eighth-best university overall, according to the Times Higher Education‘s 2022 World University Rankings, released today.
The United Kingdom’s University of Oxford ranked first among private and public universities worldwide, followed by Harvard University, the California Institute of Technology, Stanford University, the University of Cambridge, MIT and Princeton.
After UC Berkeley, Yale University and the University of Chicago rounded out the top 10.
As for the top five U.S. public universities, after UC Berkeley in first place, UCLA ranked second and in 20th place globally, followed by the University of Michigan, (24th); the University of Washington (29th) and UC San Diego (34th).
The Times Higher Ed World University Rankings evaluated more than 1,600 universities across 99 countries and territories based on five criteria: Teaching (the learning environment), research (reputation and volume income), citations (research influence), industry income (knowledge transfer) and international outcome.
Overall, UC Berkeley ranked sixth in the world for research with a score of 96 points out of 100; 14th for teaching (85.7 points); 21st for citations, (99.1 points) 104th for industry income (84.7points) and 235th for international outlook (staff, students and research) with a score of 77.6 points."
View the complete list of Times Higher Education 2022 World University Rankings rankings.
9/8/21
Forbes #1 College
9/4/21
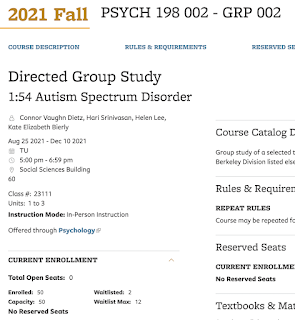
Sixth Semester teaching the Autism DeCal
50 and waitlisted!!
Got Approval for 50 students this time.
9/3/21
Inspiration Porn
Autism Lexicon: Inspiration Porn
Inspiration porn was coined by disabled comedian Maysoon Zayid and popularized by the disabled activist Stella Young in her Ted Talk. (I had initially thought it was coined by Stella Young, just due to the popularity of her Ted Talk, till I was corrected by disability activity Rebecca Cockley who knew both)